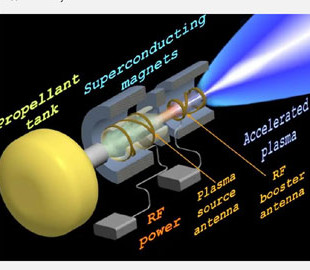
Ad Astra Rocket and Space Nuclear Power Corporation (SpaceNukes) have joined forces to develop revolutionary technologies for nuclear electric propulsion in space. The collaboration focuses on integrating the Variable Specific Impulse Magnetoplasma Rocket (VASIMR) engine with the Kilopower nuclear reactor to significantly improve the efficiency and capabilities of interplanetary missions, Phys.
VASIMR, which has been in development at Ad Astra for over 20 years, is a magnetoplasma engine that provides long-term slow acceleration in space. Such a system requires a significant power supply, which is currently limited to technologies such as solar panels or radioisotope generators (RTGs). The latter have been successfully used in space, but do not provide enough power for engines like VASIMR.
This is where Kilopower, developed by SpaceNukes, comes into play. In 2018, the company successfully demonstrated a ground-based prototype of a 1 kW reactor, and is currently working on upgrading it to 12 kW for flight testing. In the long term, the goal is to create a system with a capacity of over 100 kW, which would make nuclear electric propulsion in space a real technology.
The joint program envisages a test launch by the end of the decade, and commercialization — in the 2030s. If the project is successful, it will reduce the duration of the journey to Mars to a few months, as well as expand the possibilities of exploring distant objects in the solar system, such as Enceladus and Titan.

